Breathing is something so familiar and unconscious for a person that we do not even notice how we inhale and exhale. However, without this seemingly simple process, life is impossible. Let’s understand how the human lungs work and their inner structure facts.
Interesting facts about human lungs function will allow you to learn a lot about them. Let us dive into that immediately.
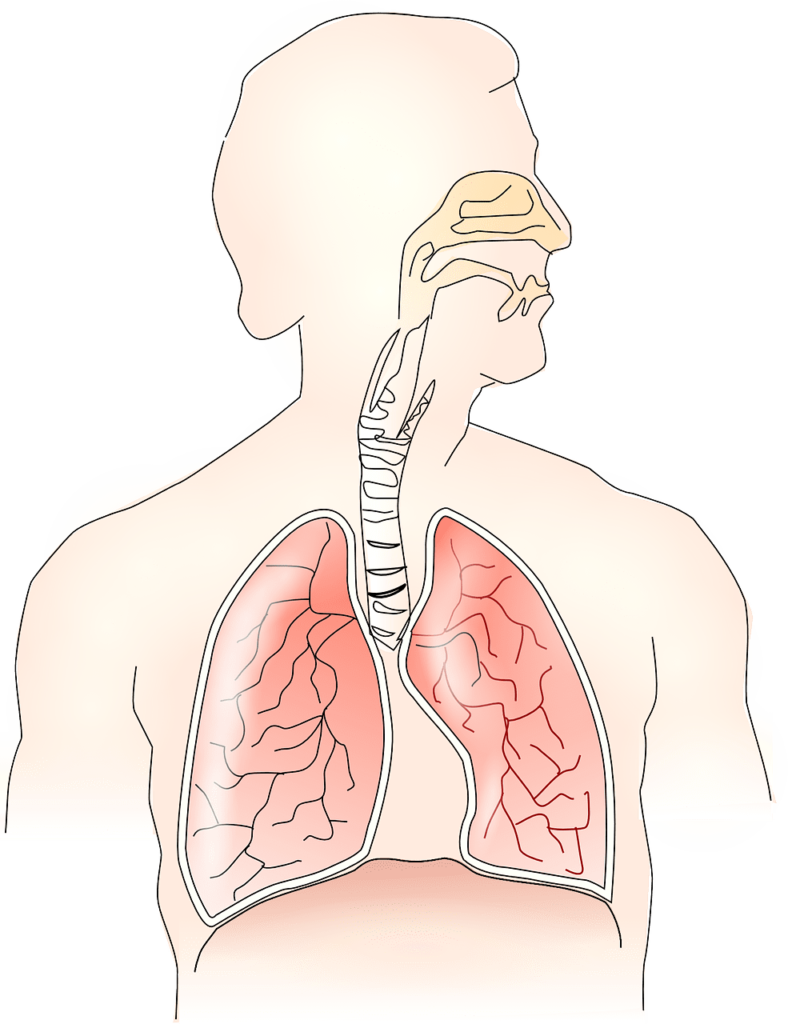
Interesting facts Human Lungs :
Lungs organ is present in humans, animals, birds, and even some species of fish. Thanks to the perfect structure of the respiratory system, all creatures in the world live.
- Lungs are the only part of the human and animal body that does not sink in water. Other organs do not have this property.
- The average person inhales 6.2 liters of air per minute.
- Because of the heart, a person’s right lung is slightly larger than the left one.
- The right lung has three lobes, and the left one has two.
- The lungs change color during their lifetime. In a newborn child, the lung tissue has a pale pink hue. With age, due to the inhalation of dust and other air impurities, the color gradually darkens.
- Breathing involves a lot of muscles. The lungs themselves cannot expand or contract. A person breathes due to the work of the abdominal muscles, diaphragm, and intercostal muscles. In this case, the inhalation and exhalation are performed due to the difference between the pressure inside the organ and the atmospheric pressure.
- Your lungs are controlled by the brain, which informs them about how much air the body needs at a particular time. Throughout the day, there are changes in breathing, and you do not even notice.
- A huge amount of blood passes through the lungs every day. The heart accelerates the blood over the area of the alveoli and returns it in just one and a half seconds. The total weight passing through this organ per day is approximately 7 tons.
- Even with one lung, you can live a full life.
- The lungs are the only organ in your body that, once in the water, will float freely. This is explained by the fact that a liter of air is always stored in the lungs (even when they exhaled).
- Human lungs have a huge size. If you expand them completely, you can cover a tennis court.
- When you inhale, the body consumes only 5% of the total amount of oxygen received.
- Every hour we exhale about 17 milliliters of water.
- The lungs can self-clean: with each exhalation, 70% of the waste that entered the body during breathing is removed.
- The lungs are directly connected to the spinal cord. Located in the chest, the lungs protect our heart, softening any blows.
- You never see your lungs, but the oral cavity is connected to them by the esophagus. Therefore, choking, you can suffocate.
- When a child is in the womb, his lungs are filled with fluid. After being born, the baby needs about 10 seconds to take the first breath.
- Human speech largely depends on the lungs. When you exhale, the flow of air passing through the larynx, where the vocal apparatus (vocal fold) is located, is converted into sound.
- An adult takes an average of 16 breaths per minute.
- The lungs produce mucus, which performs a protective function in the oral and nasal cavities.
- Exhalation is just as important for the body as inhaling. If a person did not exhale, he would very quickly receive a fatal dose of carbon dioxide.
- The lungs generate half of all platelets and contain a large supply of blood stem cells.
- Blood in the lungs is necessary, but it is also the cause of the active reproduction of bacteria.
- There is a close relationship between the lungs and the brain. Chemical compounds, getting into the lungs with inspiration, very quickly get to the brain through the blood vessels.
How to protect Human Lungs :
- Smoking is the main cause of lung cancer since the tar contained in cigarettes remains in the lungs forever.
- Deep breathing helps to get rid of pain, relax, relieve stress. This knowledge is widely used in yoga and meditation.
- Even if you do not smoke and regular exercise, the poor environmental situation in the region of residence will in any case negatively affect the health of the lungs.
Conclusion :
We have covered the detailed functional behaviors of human lungs and their natural uses to humans and animals.
and Don’t stop reading continue to explore and get excited. Some more interesting topics are given below for you.
- Human Heart: Functions, Structure & Facts
- Describe human blood and give its functions ? | 20 True facts about Human Blood
- How Human Body systems work together? 20 Facts to Know about Human Body?
- How Human lungs Work? Everything You Need To Know About Human Lungs
- 14 health benefits of guava fruit for weight loss and nutrition facts
- 20 Interesting facts about Human Teeth
- 40 Interesting facts about human eyes
- 30 Interesting facts and health benefits about watermelon
- 23 Health Benefits of Pomegranates
- Apple : Health Benefits, Fruit Information, Nutrition

